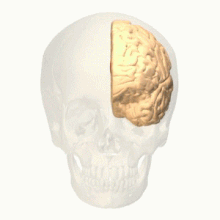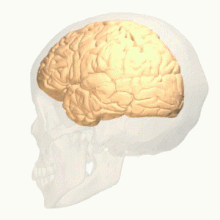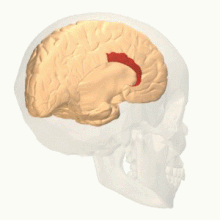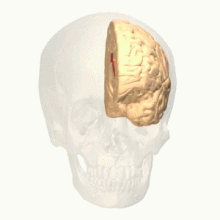
| Anterior cingulate cortex | |
|---|---|
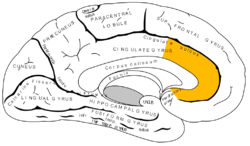
Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted
| |

Medial surface of right hemisphere, with Brodmann's areas numbered
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cortex cingularis anterior |
| NeuroNames | 161 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_936 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is the frontal part of the cingulate cortex that resembles a "collar" surrounding the frontal part of the corpus callosum. It consists of Brodmann areas 24, 32, and 33.
It appears to play a role in a wide variety of autonomic functions, such as regulating blood pressure and heart rate.[citation needed]
It is also involved in certain higher-level functions, such as attention allocation,[1] reward anticipation, decision-making,[2] ethics and morality,[3] impulse control (e.g. performance monitoring and error detection),[4] and emotion.[5][6]
Contents
Anatomy[edit]
The anterior cingulate cortex can be divided anatomically based on cognitive (dorsal), and emotional (ventral) components.[7] The dorsal part of the ACC is connected with the prefrontal cortex and parietal cortex, as well as the motor system and the frontal

No comments:
Post a Comment